A fact sheet to support the Soil CRC’s ‘Soil biology overview’ webinar, delivered as part of our ‘Building technical capacity for improved soil management’ webinar series.
In this webinar, Dr Justine Cox from the NSW Department of Primary Industries provides a thorough overview of:
- soil biological diversity and function (the good and the bad)
- a practical guide to understanding, managing and monitoring in the field
- the influences on soil biology by such things as pesticides.
Soil organisms
Soil organisms are most active in the top 30cm of soil. They range in size from microorganisms like bacteria and fungi to larger macro-organisms such as beetles and ants. Each organism plays an important role in decomposition, nutrient cycling, carbon storage, and soil structure formation.
Factors influencing soil organisms
Understanding the factors that regulate soil organisms is vital for effective soil management. Key influencers include soil type, moisture, climate, and organic matter. Texture, moisture, and climate impact soil activity, while the availability and replenishment of organic matter play a crucial role in sustaining soil organisms. Oxygen levels, temperature, and pH are also critical factors, with considerations for disturbance frequency and magnitude in maintaining a healthy soil ecosystem.
Managing soil conditions for optimal biology
Effective soil management is key for fostering optimal soil biology.
- Moisture management: Maintaining soil moisture is crucial. Techniques include soil cover, mulch, cover crops, organic amendments, and irrigation.
- Organic matter: Increasing plant biomass contributes to organic matter in the soil, which benefits soil health.
- Crop rotation: Crop rotation with diverse plant species encourages a variety of microbial species.
- Ground cover: Organic matter additions and reducing soil erosion can maintain high organic matter levels. Manage stocking rates to maintain ground cover all year round.
- Aeration: Methods for soil aeration include deep-rooted plants, occasional tillage, and mechanical aerators.
- Temperature and pH: Managing temperature and pH levels (functional range 5-9, optimal near 7) can impact soil biology. Use soil cover, mulch, and amendments as needed.
- Soil organisms: Introduction of beneficial organisms like rhizobium may fix atmospheric nitrogen for plants and mycorrhizae to enhance soil health.
- Biological products: Be cautious when using commercial biological products and ensure they have research-backed efficacy.
Monitoring soil biology: methods and challenges
Consider the aim of testing, timeframes, and limitations when monitoring soil biology. Acknowledge that soil biology testing is complex and context-dependent.
In the field, monitor the number of earthworms, mites, ants, collembola, and dung beetles, and check the nodulation percentage (on legume roots) and colour in the nodules. Determine activity and biological function using decomposition monitoring of cotton strips or litter bags, or use the tea bag index. Other biological indicators include percentage ground cover, root volume and distribution, and soil structure assessments.
Laboratory tests can determine the types and estimate numbers of bacteria and fungi using plate counts, microscopy, DNA and other molecular methods. Activity and function can be determined by enzyme activity, decomposition rate, respiration and potentially mineralisable nitrogen through incubation.
Results will indicate biology under the conditions at that point in time, in that environment. It’s important to monitor over time to determine management impacts on soil biology populations, using guides like soil health cards. Build your own data set by building a personalised monitoring schedule to gather valuable data.
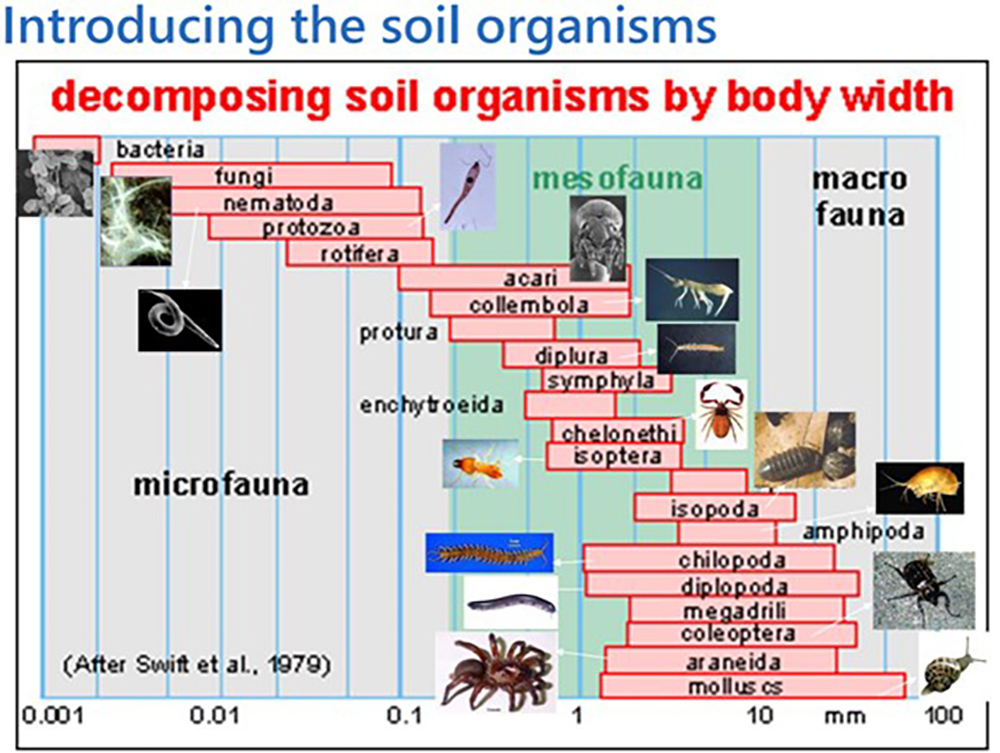
An image from the webinar showing decomposing soil organisms by body width

Related Soil CRC projects
- Project 2.1.008 Measuring soil microbes
- Project 2.3.002 Visualising Australasia’s Soils: extending the soil data federation
- Project 3.4.001 Evaluating alternative rhizobial carriers
- Project 3.4.002 Evaluation of innovative microbial carrier products
- Project 4.1.007 Building soil resilience and carbon through plant diversity
Further information
- Soil Quality: 5 Soil Biology (on Apple Books)
- Case study: Selecting and testing biological amendments (South West NRM)
- Victorian Resources Online
- Herbicide effects on soil biology (NSW Department of Primary Industries)
- SoilsWest (Western Australia)
- Soil Science Australia soil resources
- SOILHEALTH app (University of Western Australia)
Acknowledgement
This webinar was recorded in 2020 as part of the ‘Building technical capacity for improved soil management’ webinar series. It was produced by the Soil CRC and jointly funded through the Australian Government’s National Landcare Program.
Posted Apr 17, 2024

